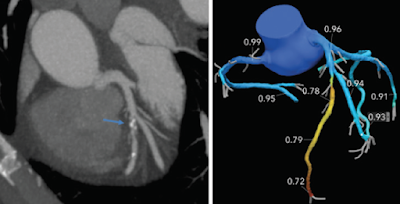
Fractional Flow Reserve, an Ideal Tool for Cardiologists to Make the Right Decision
Fractional flow reserve is an innovative technique used in cardiac catheterization to determine the blood pressure difference across coronary artery stenosis (blockage), measuring variations as a function of time. Fractional flow reserve is considered a standard technique for angioplasty and is used to evaluate the amount of oxygen delivered to the heart due to blockage. It can be defined as the pressure after blockage, relative to the pressure before blockage.
During coronary catheterization, a physician place a
specially designed catheter called a stent into an artery, using a balloon
catheter to deflate it and place the catheter tip inside the stiffened artery.
By doing so, the balloon distributes pressure across the stiffened vessel wall,
thereby measuring the amount of variation in pressure between adjacent walls. The
guidewire has a sensor on the tip, which measures the blood flow, temperature,
and pressure to determine the severity of the blockage.
The images generated from the fractional flow reserve are
sent electronically to a diagnostic imaging computer, which in turn sends these
images to a back office. Typically, the images return with data indicating the
percentage of variation in pressure that is present in the ventricle, left
ventricle, or coronary arteries. These results can then be compared with the
images obtained from the fractional flow reserve to confirm the diagnosis of
ventricular fibrillation or coronary artery stenosis. Because the images
generated from the fractional flow reserve are less clear and more prone to
error than those from the coronary artery catheterization, many physicians use
the second method of assessing the diagnosis.
However, the fractional flow reserve has been found to be an
effective and reliable method for many patients who have had their heart
monitored. According to the Robert Koch Institute, a German federal government
agency and research institute responsible for disease control and prevention,
cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in Germany, causing a
total of around 40% of all deaths.

Comments
Post a Comment